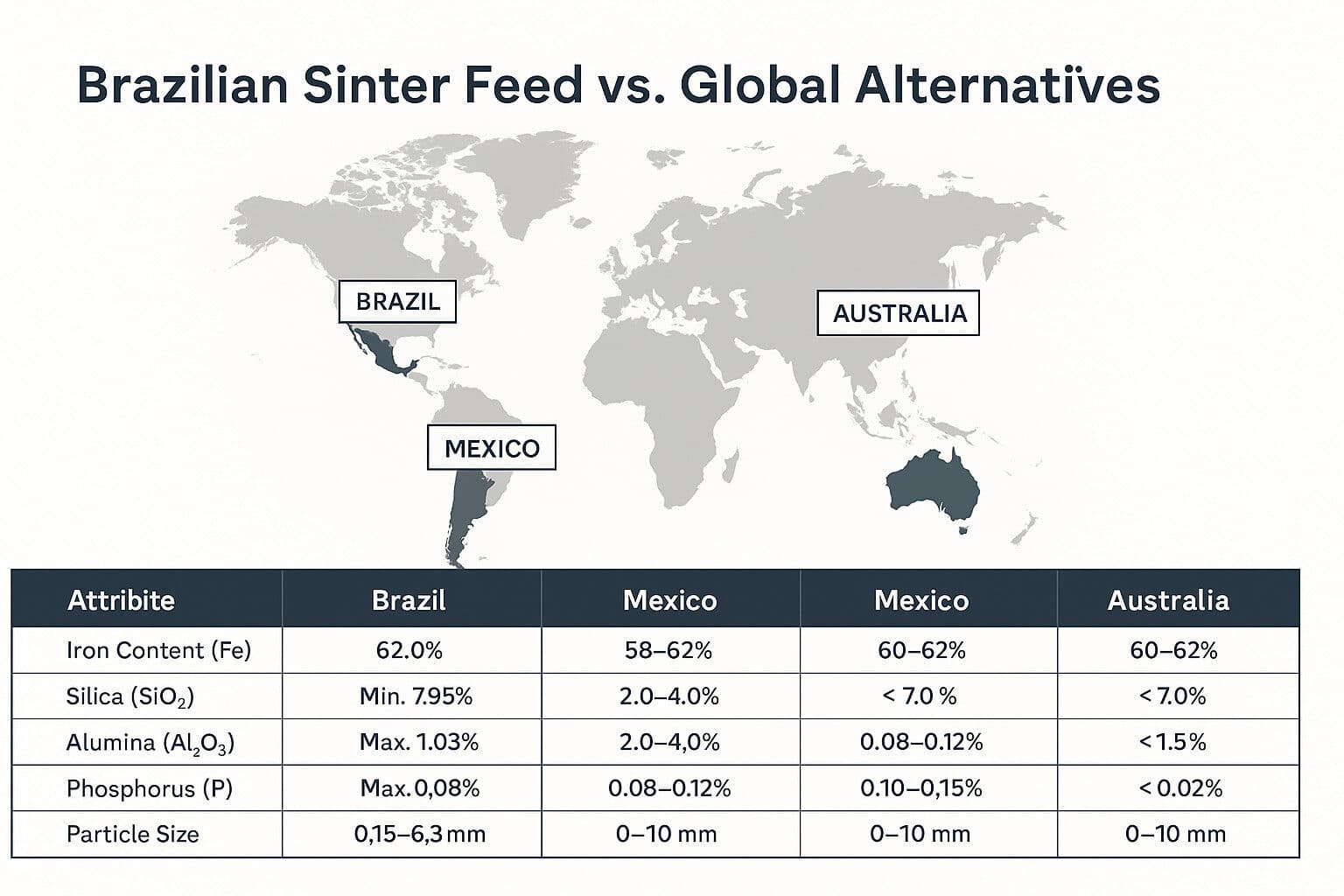
Brazilian Sugarcane: Powering Sugar & Bioethanol
Uncover the sweet success of Brazil’s sugarcane industry in sugar and bioethanol production. Explore its economic impact, cutting-edge innovations, and promising future.*
Picture yourself standing amidst a vast, undulating sea of green sugarcane, stretching to the horizon.
This is Brazil, where sugarcane isn’t just a crop – it’s the lifeblood of communities and a cornerstone of the national economy.
For centuries, this remarkable plant has been woven into the fabric of Brazilian society, supporting millions of livelihoods and shaping the country’s identity. But in recent years, Brazilian sugarcane has taken on an even more crucial role: fueling the future.
The Dual Role of Sugarcane: Sugar and Bioethanol Production
Sugar Production: A Sweet Legacy
Every time you stir sugar into your morning coffee, there’s a good chance you’re tasting a piece of Brazil. As the world’s largest sugar exporter, Brazil has perfected the art of transforming sugarcane into the sweet crystals that satisfy global cravings.
In the heart of São Paulo state, where sugarcane dominates the landscape, farmers like João Silva tend to their crops with a mix of traditional knowledge and modern precision. “My family has been growing cane for three generations,” João shares. “But now, with satellite imaging and soil sensors, we can nurture each plant like never before.”
The harvested cane rushes to nearby mills, where it’s crushed, boiled, and crystallized into sugar through a process refined over generations. Brazil’s tropical climate, nutrient-rich soil, and vast expanses of arable land create the perfect conditions for sugarcane to thrive, cementing its position as the global sugar powerhouse.
Bioethanol Production: Fueling the Future
While sugar sweetens our lives, bioethanol is revolutionizing how we power our world. Brazil stands as the world’s second-largest producer of this green fuel, with São Paulo once again leading the charge.
Dr. Maria Santos, a biochemist at a state-of-the-art bioethanol plant, explains the process: “We’re essentially performing modern alchemy. Instead of turning lead into gold, we’re transforming sugarcane juice into clean, renewable energy through fermentation and distillation.”
This isn’t just energy – it’s a liquid revolution. In 2023, Brazil produced over 35 billion liters of bioethanol, reducing CO2 emissions by approximately 90 million tons compared to gasoline use. It’s a striking example of how agricultural innovation can address global challenges.
Technological Advancements in the Brazilian Sugarcane Industry
The days of simple hoes and manual harvesting are long gone. Today’s Brazilian sugarcane industry is a high-tech marvel that would impress even the most cutting-edge Silicon Valley startup.
Innovations in Cultivation
Imagine a fleet of drones buzzing over endless sugarcane fields, providing real-time data to farmers. This isn’t science fiction – it’s precision agriculture in action. Using GPS technology and advanced imaging, farmers can monitor their crops with pinpoint accuracy, optimizing everything from water usage to pest control.
Carlos Mendes, a drone operator turned agronomist, marvels at the change: “Ten years ago, I was manually checking plants for diseases. Now, I can survey 500 hectares in a day from my computer screen, identifying potential issues before they become problems.”
But the innovation doesn’t stop there. In laboratories across Brazil, scientists are playing genetic matchmakers, developing new sugarcane varieties that are hardier, sweeter, and more efficient. These super-canes are resistant to pests and diseases, and they pack more sugar punch per stalk – a win-win for both sugar and bioethanol production.
Advancements in Processing
Step into a modern Brazilian sugar mill or bioethanol plant, and you might think you’ve wandered onto a spaceship. Automation reigns supreme, with cutting-edge machinery processing vast quantities of sugarcane with incredible speed and precision.
Ana Rodrigues, a veteran plant manager, reflects on the transformation: “When I started 30 years ago, much of our work was manual. Now, AI-powered systems optimize every step of production. We’re not just more efficient; we’re producing a higher quality product with less waste.”
This technological revolution not only ramps up productivity but also ensures a consistently high-quality end product, maintaining Brazil’s competitive edge in the global market.
Economic Impact of the Brazilian Sugarcane Industry
The economic footprint of Brazil’s sugarcane industry extends far beyond the fields and processing plants. It’s a force that shapes communities, drives regional development, and contributes significantly to the national economy.
From Fields to Fortunes
The numbers tell a compelling story. In 2023, the sugarcane industry contributed approximately 2.3% to Brazil’s GDP, generating over $50 billion in revenue. But these figures only scratch the surface of the industry’s true impact.
Job Creation: A Sweet Deal for Workers
Meet Paulo Ferreira, a former subsistence farmer who now works as a precision agriculture specialist. “Sugarcane changed my life,” Paulo says. “I went from struggling to feed my family to putting my kids through college. And I’m not alone – this industry has lifted entire communities out of poverty.”
Paulo is one of the 1.2 million people directly employed by the sugarcane sector, with an additional 3 million indirect jobs supported by the industry. From farmers tending the fields to scientists in high-tech labs, the sugarcane sector is a job-creating powerhouse.
Export Revenue: Sweetening the National Economy
Every time a ship loaded with Brazilian sugar or bioethanol leaves port, it carries more than just goods – it carries economic opportunity. In 2023, Brazil exported 32.5 million tons of sugar, earning $11.8 billion. This influx of foreign currency helps stabilize the Brazilian real and fuels economic growth.
Rural Development: Planting Seeds of Progress
The impact of the sugarcane industry on rural development is profound. In regions like São Paulo’s interior, once-sleepy villages have transformed into thriving communities. New roads connect isolated areas, modern schools educate the next generation of agronomists, and state-of-the-art hospitals provide vital healthcare.
Mariana Costa, a local government official in a sugarcane-producing municipality, notes: “The industry doesn’t just bring jobs; it brings progress. We’ve seen a 40% increase in our education budget and a 30% rise in local businesses over the last decade, all thanks to sugarcane.”
Challenges Faced by the Brazilian Sugarcane Industry
Despite its sweet success, the sugarcane industry faces some bitter challenges that threaten to upset the balance.
Climate Change: A Growing Concern
Climate change isn’t an abstract concept in Brazil’s sugarcane fields – it’s a daily reality. Luiz Oliveira, a third-generation sugarcane farmer, shares his experience: “My grandfather taught me to read the skies, but now? The weather’s become unpredictable. We’re seeing longer dry spells, more intense heat waves, and erratic rainfall patterns.”
The Brazilian Panel on Climate Change projects that by 2050, climate change could reduce sugarcane yields by up to 15% in some regions. This looming threat is driving significant investments in drought-resistant varieties and water-efficient farming techniques.
Market Fluctuations: Riding the Sugar Rollercoaster
Global sugar prices can be as volatile as a rollercoaster ride, sometimes swinging by as much as 200% in a single year. These fluctuations can make or break entire communities that depend on sugarcane.
Economist Dr. Camila Rocha explains: “The sugar market is influenced by a complex web of factors – from global production levels and consumption trends to currency exchange rates and trade policies. For Brazil’s producers, it’s a constant balancing act.”
Competition: Sweet Rivals and Fuel Competitors
The sugarcane industry isn’t just competing against itself – it’s up against a world of alternatives. Artificial sweeteners are taking a bite out of the sugar market, while electric vehicles are challenging bioethanol’s position in the fuel sector.
Roberto Alves, CEO of a major sugarcane processing company, acknowledges the challenge: “We’re not just farmers anymore – we’re energy producers, biotechnology innovators, and global commodity traders. Staying competitive requires constant innovation and diversification.”
Future Prospects of the Brazilian Sugarcane Industry
Despite these challenges, the future of Brazil’s sugarcane industry looks as bright as a freshly cut stalk in the morning sun. Here’s why:
Research and Development: Breeding Success
In labs across Brazil, scientists are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with sugarcane. Dr. Fernanda Lopes, a geneticist working on developing climate-resilient sugarcane varieties, shares her excitement: “We’re on the verge of a breakthrough. Imagine sugarcane that can thrive in drought conditions or varieties with twice the sugar content. These aren’t just pipe dreams – they’re the focus of our research, and they could revolutionize the industry.”
Technological Innovations: From Field to Future
The integration of cutting-edge technology is transforming every aspect of the industry. Drones and satellites provide real-time crop health data, self-driving harvesters move with precision through the fields, and artificial intelligence optimizes production processes.
Tech entrepreneur Rafael Menezes, whose startup develops AI solutions for sugarcane processing, notes: “We’re applying machine learning algorithms to predict optimal harvest times, maximize sugar extraction, and streamline bioethanol production. The potential for efficiency gains is enormous.”
Global Demand: A World Hungry for Sugar and Fuel
As the world’s population grows and developing economies expand, the demand for both sugar and renewable fuels is set to skyrocket. The International Sugar Organization projects global sugar consumption to increase by 1.6% annually over the next decade. Meanwhile, the global bioethanol market is expected to reach $130 billion by 2030.
Energy analyst Sofia Carvalho is optimistic: “Brazil’s sugarcane industry is uniquely positioned to meet this growing demand. With its scale, efficiency, and commitment to sustainability, it’s not just participating in the global market – it’s shaping its future.”
Sweet Success and a Green Future
As we conclude our journey through Brazil’s sugarcane industry, it’s clear that this is no ordinary agricultural sector. It’s a dynamic force that fuels economies, drives innovation, and shapes the very landscape of Brazil. From the vast fields of São Paulo to the cutting-edge bioethanol plants, the industry stands as a testament to human ingenuity and nature’s bounty.
Looking ahead, the future of Brazil’s sugarcane industry seems as vibrant as a field of cane under the tropical sun. As global challenges like climate change and energy security loom large, Brazil’s sugarcane sector is poised to offer sweet solutions for a greener future.
In the end, the story of Brazilian sugarcane is more than just about sugar or fuel. It’s a narrative of resilience, innovation, and the enduring bond between a nation and its land. As Brazil continues to lead the way in sugarcane production and bioethanol innovation, one thing is certain: the future is looking pretty sweet indeed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: How does bioethanol production benefit the environment?
A: Bioethanol reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to gasoline, significantly contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Q: Which regions in Brazil are major producers of sugarcane?
A: São Paulo leads production, accounting for about 55% of Brazil’s sugarcane. Other key regions include Goiás, Minas Gerais, and Mato Grosso do Sul.
- Q: What are the main challenges facing the industry?
A: Climate change, market price volatility, and competition from alternative sweeteners and fuels are key challenges.
- Q: How is technology changing the industry?
A: Technology is revolutionizing every aspect of the industry, from precision agriculture using drones and satellites to advanced fermentation techniques for bioethanol production.
- Q: What’s the historical significance of sugarcane in Brazil?
A: Sugarcane has been cultivated in Brazil since the 16th century, playing a crucial role in the country’s colonization, economic development, and cultural identity.
The Sweet Stats: Brazil’s Sugarcane Industry by the Numbers
Let’s dive into some fascinating figures that illustrate the remarkable journey and current standing of Brazil’s sugarcane industry. From its historical roots to future projections, these numbers tell a story of growth, innovation, and global significance.
A Journey Through Time
🌱 1500s: Sugarcane cultivation begins in Brazil, laying the foundation for centuries of sweet success.
🚀 1975: Launch of the Proálcool program, revolutionizing the industry by promoting bioethanol production.
Today’s Sugar Rush
🏆 World’s Largest Producer: Brazil churns out over 600 million metric tons of sugarcane annually.
🥇 Export Champion: Accounting for about 40% of global sugar exports, Brazil sweetens the world.
🌿 Green Energy Powerhouse: With an annual production exceeding 30 billion liters, Brazil ranks as the second-largest bioethanol producer globally.
👥 Job Creator: The industry employs over 1 million people directly, supporting countless families and communities.
Forecasting a Sweet Future
📈 Growing Global Sweet Tooth: Worldwide sugar demand is projected to increase by 2% annually, driven by population growth and rising consumption in developing nations.
🚗 Fueling the Future: Global bioethanol demand is expected to surge by 5% yearly, as the world thirsts for renewable energy solutions.
🌾 Expanding Horizons: Brazil’s sugarcane production is set to grow by a staggering 30% over the next decade, solidifying its position as a global leader.
These numbers not only highlight the current strength of Brazil’s sugarcane industry but also point to a future brimming with potential. As the world increasingly seeks sustainable solutions for food and energy, Brazil’s sugarcane sector stands ready to meet the challenge, promising continued growth, innovation, and global impact.